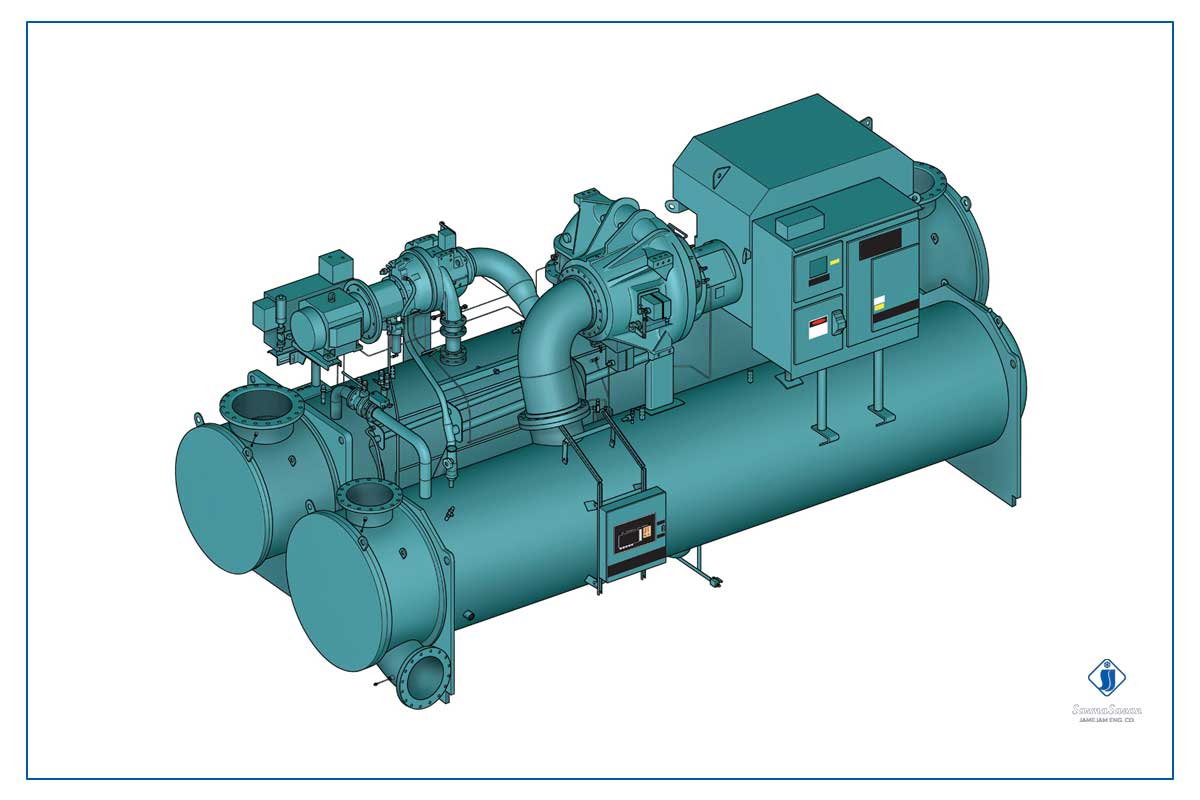
What is a centrifugal or centrifugal chiller?
A centrifugal chiller, like any other chiller that is part of an air conditioning system, is a device that uses thermodynamic laws to dissipate heat and balance temperature. But what is this chiller? It should be said that the word centrifuge in this chiller refers to its compressor section.
It can be said that there are different categories for chillers. The variety of components inside the building of a chiller and the type of those components can determine the overall type of chiller. For example, the presence of a compressor in a chiller itself determines the type of chiller. Since two general types are defined for chillers and absorption chillers do not use the compressor inside their building, wherever the name of the compressor is mentioned in the chiller, it means that the named chiller is of the compression type. As here, the type of chiller compressor determines the general type of a compression chiller. So when it comes to the word centrifuge in this chiller, it means that the compressor is centrifugal or centrifugal.
Regarding the applications of this chiller, it can be said that since centrifugal chillers have high capacity and efficiency, the application and use of centrifugal chillers includes heavy and large projects.
Centrifuge operation
In general, in any compression chiller, there is a main cycle between its components, which includes the evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion valve. Meanwhile, the compressor in a chiller is responsible for compressing the refrigerant. This device is located in the chiller cycle, between the evaporator and the condenser. The chiller compressor works by taking the gas refrigerant from the evaporator, increasing the temperature and pressure, and finally transferring it to the condenser to dissipate heat to continue the cycle.
Since the gas refrigerant pressure is not high enough when it enters the compressor, the rotation of a propeller is used to generate its driving force to increase the gas refrigerant pressure. In a centrifugal chiller, the structure of a centrifugal compressor is such that it uses a propeller or impeller to flow the gas refrigerant and create a centrifugal force. Thus, in this compressor by the centrifugal force, the kinetic energy of the gas refrigerant increases the refrigerant pressure and in the continuation of this event, the gas refrigerant also increases the temperature.
For this compressor, there are two inlet and outlet ducts in the form of a suction duct and discharge duct to take the gas refrigerant from the evaporator and after the process, direct it to the condenser. This is what a compressor should do because the main task of the compressor in chillers is to compress the refrigerant. In general, the efficiency of a centrifugal chiller or centrifuge is directly related to the speed of its impeller.
Types of centrifugal chillers
Turbocharger centrifuge
Turbocharger centrifugal chiller or turbocharger chiller is a centrifugal chiller that works without oil, without mechanical contact and without friction. This means that the chiller of the turbocharged centrifuge chiller is based on a magnet. In a turbocharged centrifugal chiller, the impeller creates a magnetic field during operation and rotation, so that no contact is made with the magnetic bearings.
As a result of this type of operation, the turbocharger compressor has a long service life. Other advantages of the turbocharger compressor include noise pollution and low vibration. Also, the weight and volume of these compressors are significantly less than similar models. However, this mode of operation requires precise and digital control of the device. This compressor also has a refrigerant suction duct to enter and a refrigerant discharge duct to move to the condenser, and for better performance and repetition of the impellers, two impellers are used inside a turbocharger compressor.
Cool water centrifuge chiller and air cooler
For centrifugal chillers, like any other compression chiller, two types of cold water and cool air are defined. Speaking of these two types, it goes back to the type of operation of the chiller condenser. It basically means what the driving force of a condenser is and whether a condenser uses water or the surrounding air to cool itself.
If the centrifugal chiller is cold water, it means that the condenser is using it for cooling and it needs a chiller cooling tower. Thus another device called a cooling tower; Excess components in the chiller cycle are added to it. In this way, the water in the cooling tower, by transferring heat and exchanging temperature, dissipates the heat in the condenser and lowers the refrigerant temperature. The use of a cooling tower in a centrifugal chiller has its issues. The need for more maintenance and care, increasing the weight and volume of the chiller and high water consumption are some of the negative aspects of having a cooling tower in a cold water centrifugal chiller.
Air-cooled centrifugal chiller but no additional attachment required. This means that the condenser discharges the heat in the surrounding air and in fact the outside air.
Closed, semi-closed and open centrifugal chiller
There are three types of open, closed and semi-closed systems for centrifugal chillers. The opening and closing of these chillers depend on how the mechanical and electrical parts of the chiller are connected. In fact, different parts of a chiller are formed, each of which was used in a special way. In a centrifugal chiller, mechanical equipment such as impellers are considered mechanical parts, and the chiller motor is powered by electricity to provide propulsion to the mechanical parts.
The placement of these parts can be done in a single and connected form with the name of closed circuit, which provides few facilities for chiller repair. Also, there is another method called open circuit to connect these two parts, which puts them completely apart. The disadvantage of this system is the risk of leakage of chiller refrigerant.
The third type of centrifugal chiller, which has a semi-closed circuit, is an open circuit-like system in which the two parts are separated but placed inside a chamber.

 English
English  فارسی
فارسی